Tech Briefs
Savannah River National Laboratory
Development of a Passivated Stainless Steel Surface
Technology Overview
Savannah River National Laboratory (SRNL) has developed a process to passivate stainless steel surfaces that is more elaborate than the process traditionally termed passivation. This new process better renders the surface inert to hydrogen out-gassing and inhibits the reaction of the substrate with hydrogen and water better than previously existing technologies.
Benefits
- Inhibited gas migration in stainless steels
- Minimizes catalytic breakdown of gases in storage
- Increases shelf life of tritium gas standards
Applications
- Corrosion prevention in stainless steels in industry and bio-medical devices
- Treatment of gas storage bottles and equipment
- Pretreatment for high-temperature uses of stainless steel
Description
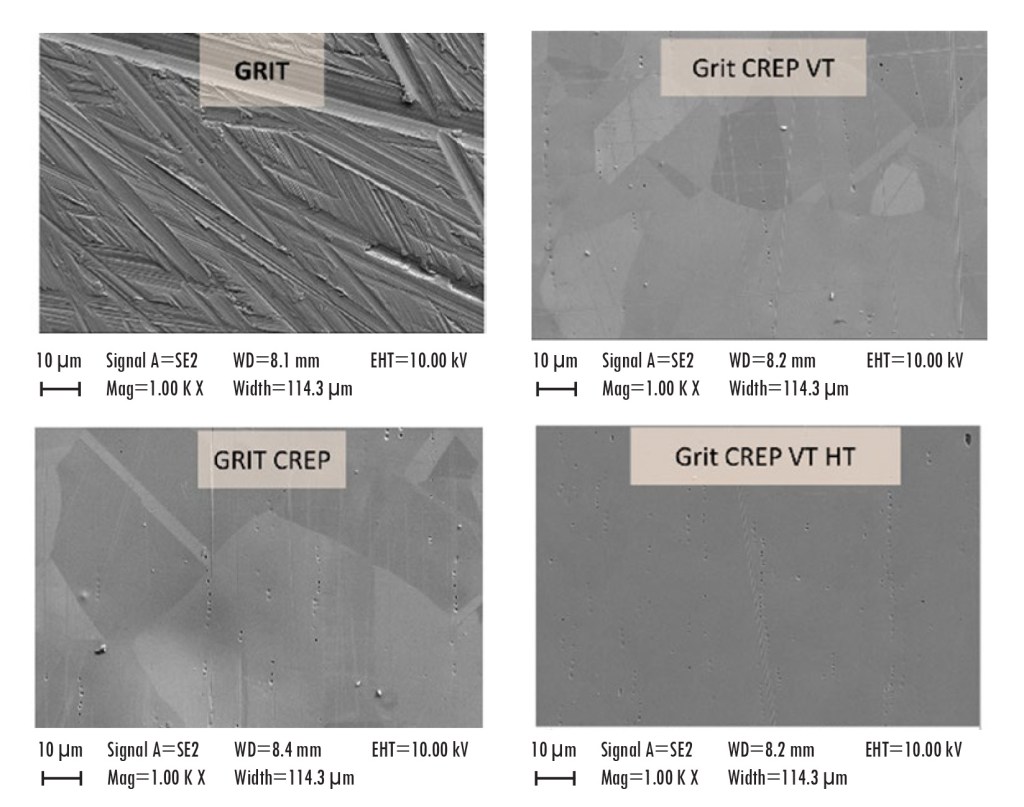
To improve handling and storage of hydrogen isotopes, a stainless steel passivation process has been developed that includes electropolishing and vacuum treatment with associated secondary operations, termed Q-passivation. Q-passivation can smooth the surface, remove residual hydrogen, and create a chromium and chromium oxide rich surface. The enriched surface can inhibit migration of hydrogen liberated from bulk stainless steel and can limit surface interaction by diminishing catalytic metal centers on the surface that can react with hydrogen and water. This novel process results in a stainless steel surface that is inert to tritium, minimizing isotope exchange between hydrogen and deuterium and minimizing catalytic breakdown at the surface.
Intellectual Property
This technology and methods for its use have been granted U.S. Patent No. 10,450,668 B2 (October 22, 2019), “Development of a Passivated Stainless Steel Surface” and is available for licensing.
Partnering Opportunities
SRNL invites interested companies with proven capabilities in this area of expertise to develop commercial applications for this process under a cooperative research and development agreement (CRADA) or licensing agreement. Interested companies will be requested to submit a business plan setting forth company qualifications, strategies, activities, and milestones for commercializing this invention. Qualifications should include past experience at bringing similar products to market, reasonable schedule for product launch, sufficient manufacturing capacity, established distribution networks, and evidence of sufficient financial resources for product development and launch.
Download Tech Brief
Contact Information
Savannah River National Laboratory
E-mail: partnerships@srnl.doe.gov