Plant-Based Contaminant Monitoring at SRNL: Implementation
The U.S. Army Corps of Engineers began utilizing Bahia grass, a drought and heat tolerant plant, for environmental remediation in March of 2023. After an introduction from the Department of Energy Office of Fossil Energy and Carbon Management, Savannah River National Laboratory (SRNL) became a collaborator on the project, providing expertise in machine learning for long-term contaminant monitoring.
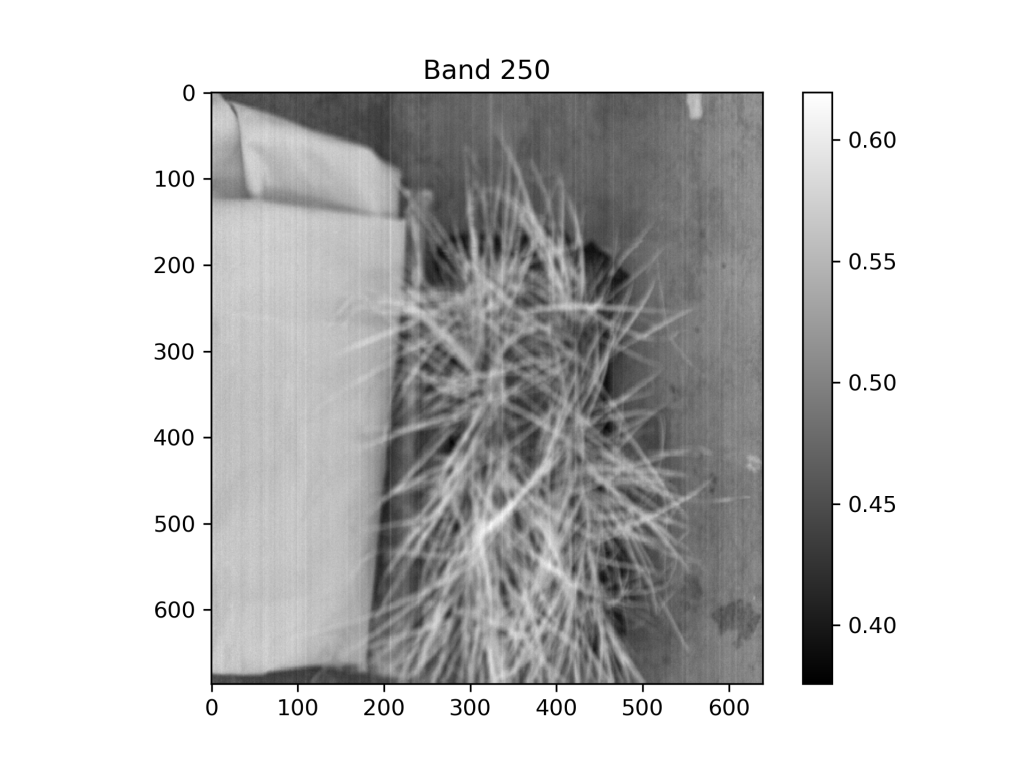
As experiments progressed, SRNL identified an additional function for the phytoremediation. When photographed with a hyperspectral camera, the grass can also function as a sensor, providing critical data on the contaminants contained in the grass. Hyperspectral images detect information from the electromagnetic spectrum for each pixel of a captured image. These images can be used to characterize specific materials by matching data from the photo to the unique spectral signatures of an individual material. Hyperspectral imaging is commonly used in the food and pharmaceutical production industries for quality control. In the context of this project, hyperspectral imaging is aiding in identification of the concentration of groundwater contaminants taken up by the grass.

As a plant responds to contaminant interactions (e.g., by “wilting”), the hyperspectral signature changes. SRNL is training a machine learning algorithm to identify the amount of contamination that has been taken up based on changes to the image over time. Below are example images captured by a hyperspectral camera after the grass has been exposed to contaminants placed in the soil.
”Working with SRNL on this joint project funded by the Department of Energy Office of Fossil Energy and Carbon Management showcases their novel use of bioindicators and the importance of research and development alongside environmental justice,” said Franz Lichtner, USACE research ecologist at the Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, Hanover, New Hampshire. “The SRNL team has been interested in applying modeling techniques to scale data applications from greenhouse to field scale.”
After initial data collection, SRNL has developed a preliminary proof of concept utilizing a clustering algorithm to group similar pixels captured in the hyperspectral images.